Quote of the week
"In the midst of chaos, there is also opportunity"
- Sun Tzu

Edition 20 - May 18, 2025
"In the midst of chaos, there is also opportunity"
- Sun Tzu

Google I/O 2025, set to commence on May 20, is shaping up to be a pivotal moment for the tech giant. With the rapid evolution of AI technologies and increasing competition from rivals like OpenAI and Perplexity AI, Google's announcements at this event could significantly influence its position in the AI-driven future.

One of the most anticipated unveilings is "Codey," an autonomous coding assistant designed to aid developers throughout the software development lifecycle. From task management to code documentation, Codey aims to streamline workflows and enhance productivity by automating repetitive tasks and providing intelligent code suggestions. This move not only showcases Google's commitment to supporting developers but also positions the company as a leader in AI-powered software development tools.
In addition to Codey, Google plans to introduce a visual discovery tool reminiscent of Pinterest. Leveraging AI, this tool will enhance user interaction with visual content, offering personalized recommendations based on user preferences and behaviors. By integrating this tool into its existing platforms, Google aims to provide a more intuitive and engaging visual search experience, further solidifying its foothold in the AI-enhanced user experience domain.

Beyond these product announcements, the tech community eagerly awaits clarity on Google's overarching strategy for transitioning to AI-driven search. The introduction of "AI Mode" in Google's search engine, which offers AI-generated responses to user queries, signifies a big shift from traditional search methods. Yet, questions remain about how this transition will affect users, advertisers, and the broader digital ecosystem.
In conclusion, while Google's forthcoming tools like Codey and the visual discovery platform highlight its innovative capabilities, the company's long-term success hinges on transparently communicating its AI search strategy. As AI continues to redefine the digital landscape, stakeholders will look to Google for leadership and clarity in navigating this new era.
Manus AI, the autonomous agent developed by Chinese startup Monica, has officially exited its waitlist phase, offering 1,000 free starter credits and 300 daily credits to all users. This move democratizes access to a tool that has been lauded for its ability to autonomously execute complex tasks, from coding to data analysis. Unlike traditional AI models that require step-by-step prompting, Manus operates with a multi-agent system, allowing it to plan, execute, and deliver results with minimal human intervention.
I was on the waitlist for about a month before getting access earlier this year, and I shared my first impressions in a LinkedIn post. In that first test, I gave Manus a complex investing question that I've been thinking about for a long time and got back an amazing breakdown that would’ve taken me many hours on my own. For new users, don’t waste your credits on something silly just to “try it out.” Instead, pick a thorny problem you’ve been chewing on for weeks and throw it at Manus — you might be surprised at what it returns.
TikTok has introduced "AI Alive," a new feature that transforms static photos into dynamic, short-form videos within TikTok Stories. Utilizing intelligent editing tools, AI Alive allows users to animate their images by adding movement, atmospheric, and creative effects, enhancing storytelling capabilities without requiring advanced editing skills. This feature is accessible through the Story Camera by selecting a photo and applying AI-generated enhancements, enabling creators to produce engaging content directly within the app.
To ensure responsible use, TikTok has implemented safety measures for AI Alive. Uploaded photos, user prompts, and the resulting AI-generated videos undergo moderation before being displayed to the creator. A final safety check is conducted prior to publishing the content. Additionally, all AI-generated videos are labeled accordingly and embedded with C2PA metadata, promoting transparency and helping users identify AI-created content even when shared outside the platform.
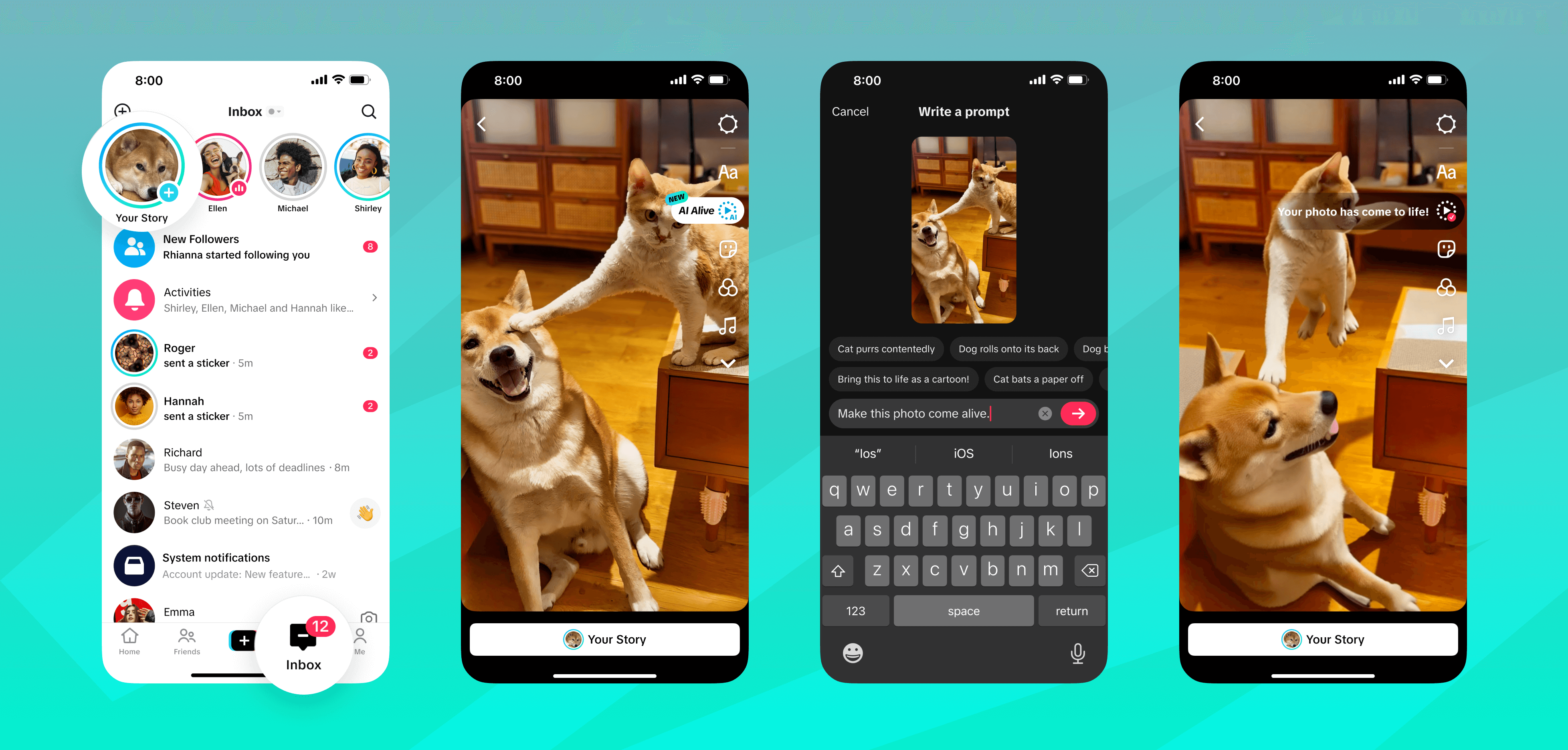
AI Alive represents TikTok's commitment to expanding creative tools for its user base, empowering individuals to craft visually compelling narratives. By integrating this feature, TikTok continues to enhance user engagement and content diversity, solidifying its position as a leading platform for innovative digital expression.
But beyond its novelty, AI Alive hints at a larger shift: product marketing and entertainment are being reshaped by generative tools that allow anyone to build immersive experiences. The smart move is not to dismiss this as a gimmick, but to treat it as an early preview of where storytelling is going. Whether you're a brand, a creator, or just curious — try animating a product concept or moodboard. You might find AI Alive more powerful than it looks.

Venus Aerospace, a Houston-based startup, has achieved a significant milestone by successfully conducting the first US flight test of a rotating detonation rocket engine (RDRE) at Spaceport America in New Mexico. Unlike conventional engines, RDREs utilize supersonic combustion waves that rotate within a circular chamber, offering enhanced efficiency and thrust. This test marks a pivotal advancement in propulsion technology, demonstrating the practical viability of RDREs for future aerospace applications.
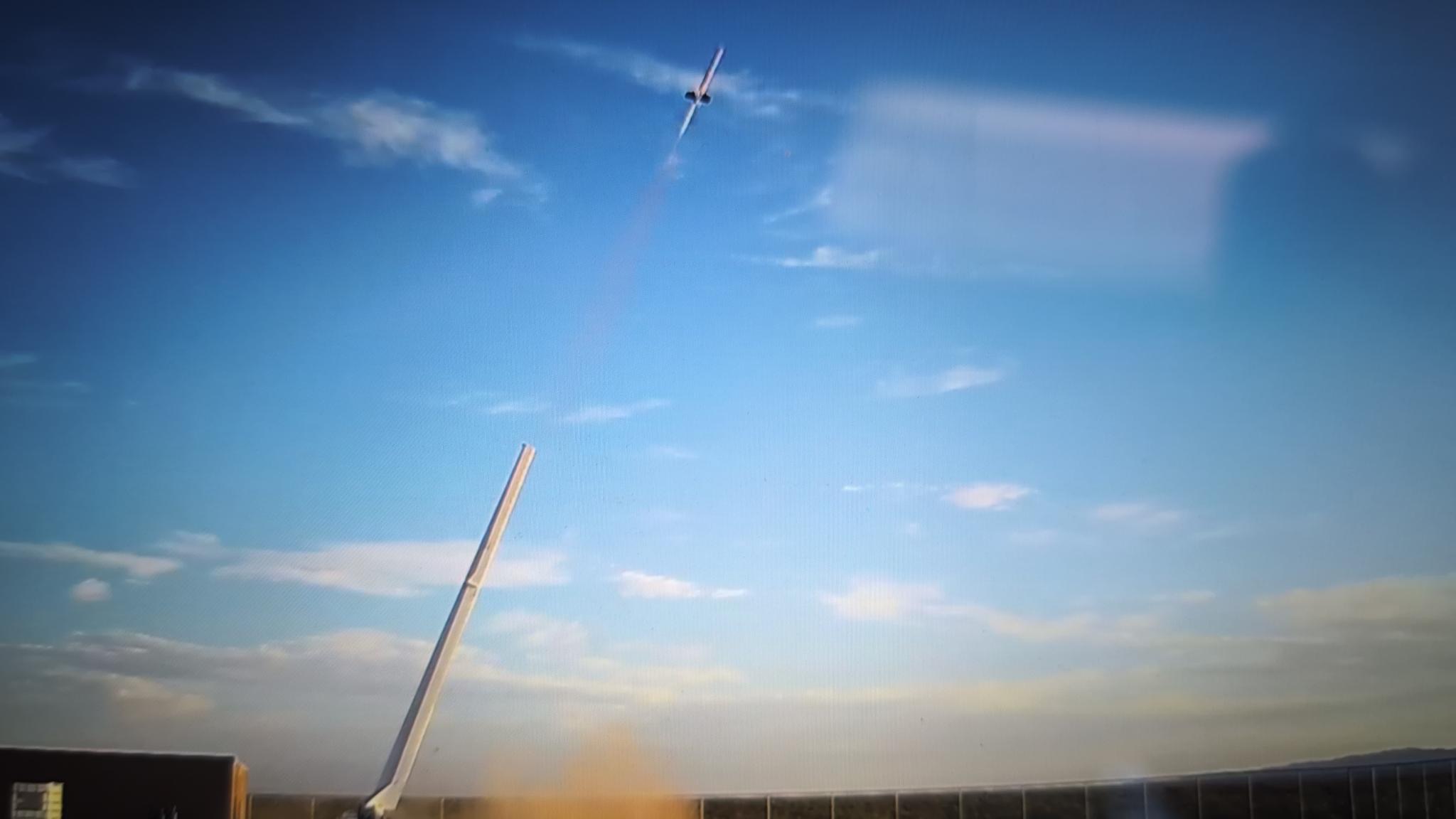

The RDRE's design allows for continuous detonation, resulting in a more compact and efficient engine compared to traditional combustion methods. By harnessing this technology, Venus Aerospace aims to revolutionize high-speed travel, potentially enabling aircraft to reach speeds up to Mach 9. Such advancements could drastically reduce intercontinental flight times, making destinations like Los Angeles to Tokyo achievable in under two hours.
Beyond commercial aviation, the implications of RDRE technology extend to defense and space exploration sectors. The increased efficiency and reduced fuel consumption make RDREs attractive for various applications, including hypersonic missiles and reusable space vehicles. Venus Aerospace's successful test not only validates the RDRE concept but also positions the company at the forefront of next-generation propulsion systems, potentially transforming the landscape of high-speed travel and aerospace engineering.
However, the introduction of RDREs also raises questions about the future of warfare and space travel. In the defense sector, the ability to develop faster and more efficient missiles could alter the balance of power, necessitating new strategies and countermeasures. In space exploration, the enhanced efficiency of RDREs could reduce the cost and complexity of missions, enabling more frequent and ambitious endeavors. As with any disruptive technology, careful consideration and regulation will be essential to ensure that the benefits of RDREs are realized responsibly.
A baby in Philadelphia has become the first to receive a customized CRISPR gene-editing therapy for a rare, life-threatening liver condition. Before treatment, the buildup of ammonia in his system stunted his growth and risked organ failure. Since the therapy, he’s gained healthy weight, now in the 35th percentile, and needs fewer medications. This case could open the door to fast, personalized treatments for other rare diseases.
The National Institutes of Health has shut down its last lab for testing drugs on beagles, acknowledging that results from dogs often don’t translate to humans. It’s a major step toward more ethical and accurate science.
Canadian researchers have confirmed a strange truth: living organisms glow—just a little—and that glow fades when they die. In mice and plants, this biophotonic light dimmed after death and flared in injured areas. It’s a poetic discovery: life, it turns out, literally shines.
Montana has enacted Senate Bill 535, significantly expanding its "Right to Try" legislation. This new law permits healthcare clinics and physicians to offer experimental drugs to patients, provided these drugs have completed at least one Phase I clinical trial. Unlike previous laws that limited access to terminally ill patients, this legislation allows any individual to seek such treatments. It also introduces a licensing system for "experimental treatment centers" and requires them to allocate 2% of annual profits to help low-income patients access therapies.

Supporters argue this will turn Montana into a medical tourism hub, especially for cutting-edge treatments like anti-aging therapies. By opening access to experimental drugs within US borders, the law could prevent desperate patients from seeking risky or unregulated care abroad. More importantly, it empowers people to make informed decisions about their own bodies—especially when no other options remain.
Of course, critics have concerns. Phase I trials only test safety, not whether the drug actually works. Ethicists worry about the commercialization of unproven treatments and what it means for regulatory standards. But for patients with no time left to wait, those debates are a luxury. If the risks are known, shouldn't they get to decide what risks they're willing to take?
The FDA's cautious approval process exists for good reason—but when it becomes a barrier to hope, something has gone wrong. Montana's law isn't perfect, but it starts from the radical idea that dying patients should have more options, not fewer. It forces us to ask: what good is safety, if it comes too late to save you?
Chinese researchers at Peking University have developed the world's fastest and most energy-efficient transistor, marking a significant departure from traditional silicon-based designs. Utilizing a two-dimensional architecture, the team constructed the transistor from bismuth oxyselenide (Bi₂O₂Se) and bismuth selenite oxide (Bi₂SeO₅), materials known for their exceptional electrical properties. This new transistor design, which replaces the conventional Fin Field-Effect Transistor (FinFET) structure with a gate-all-around field-effect transistor (GAAFET) configuration, allows for better control of current flow and significantly reduces energy loss. The result is a transistor that operates 40% faster and consumes 10% less energy than the most advanced 3-nanometer silicon chips currently available.

This innovation addresses the physical limitations faced by silicon-based transistors as they approach atomic scales, where performance gains diminish and power consumption increases. By employing bismuth-based materials, the researchers achieved higher electron mobility and a smoother interface, reducing electron scattering and current loss. This advancement not only enhances speed and efficiency but also minimizes the risk of overheating, a common issue in densely packed silicon chips. The smoother interface between the bismuth compounds further contributes to the transistor's superior performance by reducing defects and electrical noise.
Beyond the technological breakthrough, this development has significant geopolitical implications. Amidst US-led export restrictions that limit China's access to advanced silicon chip-making equipment, this silicon-free transistor represents a strategic move towards technological self-reliance. By pioneering alternative materials and architectures, China aims to circumvent these restrictions and establish a foothold in next-generation semiconductor technology. This achievement not only positions China at the forefront of semiconductor innovation but also signals a potential shift in the global landscape of chip manufacturing.
Enjoying The Hillsberg Report? Share it with friends who might find it valuable!
Haven't signed up for the weekly notification?
Subscribe Now